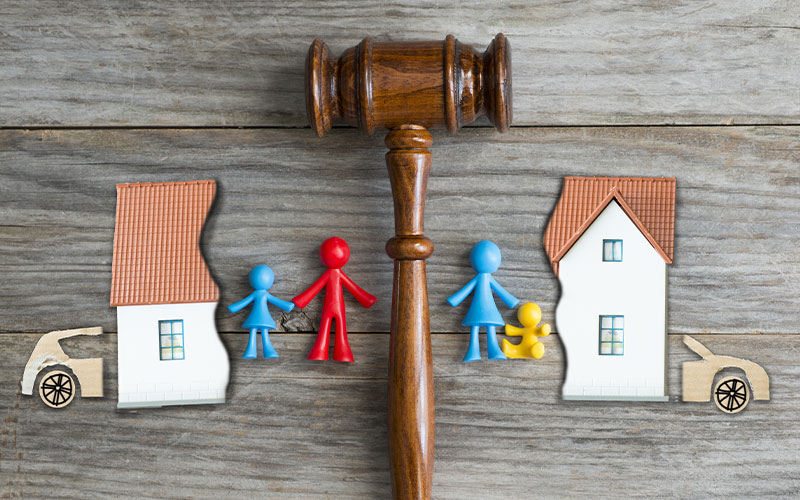
When you get a divorce in Washington State, all of your assets and debts, even those you have kept separate from your spouse, will be awarded to one party of the other. The term “property” refers to your home, vehicles, personal belongings, investments and retirement accounts, and business interests. Washington State is just one of nine U.S. states that have community property statutes, meaning the law presumes joint ownership.
How Communal Property is Divided
In a 50/50 divorce state like Washington, how much each spouse earned during the marriage doesn’t matter. All property that is considered community property — assets, debts, income, property, etc. — is subject to division.
Any property or assets that were owned before the marriage, as well as inheritances given to just one spouse, are considered separate property. But, if that separate property gets combined with community property, such as placing it in a joint bank or investment account, it can be difficult to divide.
The two parties can negotiate the division of assets. Or the courts can make these determinations. All assets and debts are labeled as either communal or separate property. Whole items like houses and cars are either given to each party or sold, and cash/stock is divided.
What Determines Equitable Distribution?
Most other states use the principle of equitable distribution instead of a 50/50 model. In those states, assets and debts are divided according to several criteria:
- Length of marriage
- Relative earning capacity of each partner
- Age and health of each partner
- Size of the estate
- Parenting Plan arrangements
Depending on the circumstances of the case, the split of assets could turn out to be even, or it could be 60/40, or some other division that is considered fair.
Situations that Prevent 50/50 Distribution
While assets and debts acquired during the marriage are considered community property in Washington, not everything will be divided equally during a divorce. Some of the situations that will prevent a 50/50 split of property include:
- A pre or post-nuptial agreement can keep certain assets separate.
- Separate property before the marriage, inheritances, and gifts for one spouse are exceptions.
- The spouse who earns the most will usually pay the majority of debts.
- Items are generally kept with the spouse who uses them the most (example – a vehicle driven for work).
While Washington State is primarily considered a 50/50 divorce state in terms of asset distribution, there are exceptions. And the parties have the opportunity to negotiate these terms outside the courtroom, which can often lead to more favorable terms.
If you have questions about how your property, assets, and debts will be divided during the divorce process, Steller Legal Group can help. Our experienced Washington divorce lawyers will advocate for your interests throughout the divorce process. Contact our office today to schedule a free consultation.